
Computer-Aided LRFD Analysis and Design of Bolted Splices for Steel Bridges
Firas I. Sheikh-Ibrahim,
Ph.D., PE
Lead Engineer
Parsons Brinckerhoff Quade & Douglas, Inc.
Pittsburgh, PA
 In
1999, the American Association of State highway and Transportation Officials
(AASHTO) adopted a new methodology
for the design of bolted field splices of flexural steel members. The new methodology
was developed in response to the lack of a uniform design methodology for bolted
splices, which resulted in confusion and costly splices.
In
1999, the American Association of State highway and Transportation Officials
(AASHTO) adopted a new methodology
for the design of bolted field splices of flexural steel members. The new methodology
was developed in response to the lack of a uniform design methodology for bolted
splices, which resulted in confusion and costly splices.
The
new methodology includes new formulas for the web and flange forces as well
as minimum design forces. It also includes new rules and formulas for girders
with holes in the tension flange as well as the resistance of flange bolts when
passing through fillers. To help engineers implement the new methodology, AISI's
Transportation and Infrastructures Committee sponsored the development of
AISIsplice
software.
AISIsplice
is a tool for the analysis and design of bolted field splices for straight,
right, I-shaped, steel girders that follows the procedures of the AASHTO LRFD
Bridge Design Specifications, Second Edition, 1998, including the 1999 interim.
The 1999 revisions to the AASHTO Specification were based on research performed
by Firas I. Sheikh-Ibrahim and Karl Frank (1996, 1998) at the University of
Texas at Austin.
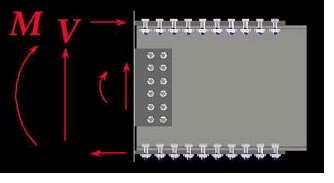 In
the design mode, the software sizes and optimizes the splice plates and bolts.
In the analysis mode, the software determines the adequacy of given splice plates
and bolts. For both modes, performance ratios (load/resistance) for all splice
components are determined.
In
the design mode, the software sizes and optimizes the splice plates and bolts.
In the analysis mode, the software determines the adequacy of given splice plates
and bolts. For both modes, performance ratios (load/resistance) for all splice
components are determined.
The software output consists of scaled graphics and a detailed report. Graphic illustrations include the elevation and cross section views of the splice and adjoined girders. Graphical output includes splice dimensions, bolt details, a summary of required filler plates, and splice component performance ratios.
When designing a splice, the Splice Design Summary screen appears. This screen contains graphical output of splice details, required filler plates and their locations, girder cross sections and elevation views, properties of the flange and web connection bolts, faying surface class, and performance ratios.
A useful feature of AISIsplice is the Adjust Design option. After a splice design is generated by the software, the user may modify the design to his/her preference. When this option is used all properties of the designed splice are loaded into the Splice Analysis module. The user may change selected properties of the splice, and then the program analyzes the splice.
In this lesson, you
need to
Download AISIsplice User's Manual (a zipped
html file, 1.60 MB)
Download
AISIsplice User's Manual
(a Word file, 1.04 MB)
The AISIsplice User's Manual can be
downloaded and be printed free of charge. Choose any of the formats below to start
downloading:
Download
AISIsplice User's Manual
(a PDF file, 3.50 MB)
Once
you finish viewing the slide show and studying the User's Manual of AISIsplice,
you need to
take a quiz
to obtain the PDH credits.
***
Additional Technical Resource
and Further Readings:
*** Acknowledgment:
PDHonline.com acknowledges the sponsorship of
American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI)
for this online course.
*** Once
you finish viewing the slide show and studying the User's Manual of AISIsplice,
you need to
take a quiz
to obtain the PDH credits.
![]()
DISCLAIMER:
The materials contained in the online course are not intended as a representation
or warranty on the part of PDHonline.com or any other person.comanization named
herein. The materials are for general information only. They are not a substitute
for competent professional advice. Application of this information to a specific
project should be reviewed by a registered professional engineer. Anyone making
use of the information set forth herein does so at their own risk and assumes
any and all resulting liability arising therefrom.
![]()
